You don’t need to know everything about color mixing to get nice clean colors in watercolor. Just the basics can help.
Colour Basics
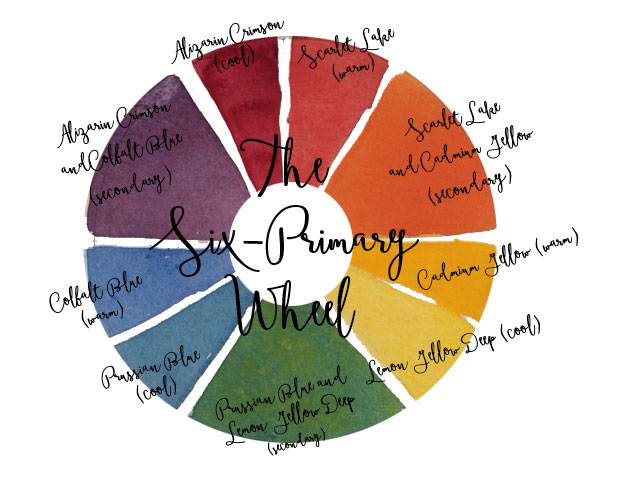
The Six-Primary Wheel above uses warm and cool primaries that mix to get secondaries.
Primaries: red, blue, yellow
Secondaries: green, violet, orange
Tertiaries: blue/green, blue/violet, red/violet, red/orange, yellow/orange, yellow/green (mix equal quantities of primary and secondary)
Hue: is the color in its purest and simplest form ie. red, blue, green
Tone or Value: lightness or darkness
Intensity: brilliance of a color
Temperature: warmth or coolness
Colour Schemes
- Monochromatic: one colour
- Complementary: color opposite on the colour wheel, blue/orange, red/green, yellow/violet, (mixing complementaries produces neutral greys and browns, and provides the most contrast)
- Analogous: colors related to each other on the color wheel ( provides a very harmonious and is good for emphasizing mood)
- Complementary/analogous: analogous colors plus one complementary ( harmony from the analogous colors and balance from the complementary, mixing produces a wider range of dulled colors and greys)
- Triadic: three colors in a triangular arrangement on the color wheel (produces the widest range of mixed colors and unique greys)
Colour Mixing
- mix colors to reduce intensity and/or grey colours
- to change hue
- to grey a color add its complement
- to alter a hue with minimal loss of intensity add the intense hue nearest it on the color scale. (ie phthalo cyanine green to go towards yellow mix with yellow lemon pale or light rather than cadmium yellow medium)
- when mixing colors always start with the lighter color and add the darker
- when two colors are similar in tone add the less transparent to the more transparent